What are e-invoices?
An electronic invoice or e-invoice is a digital document that represents invoice data in machine-readable form and in a standardized format and can therefore be processed electronically by the recipient.
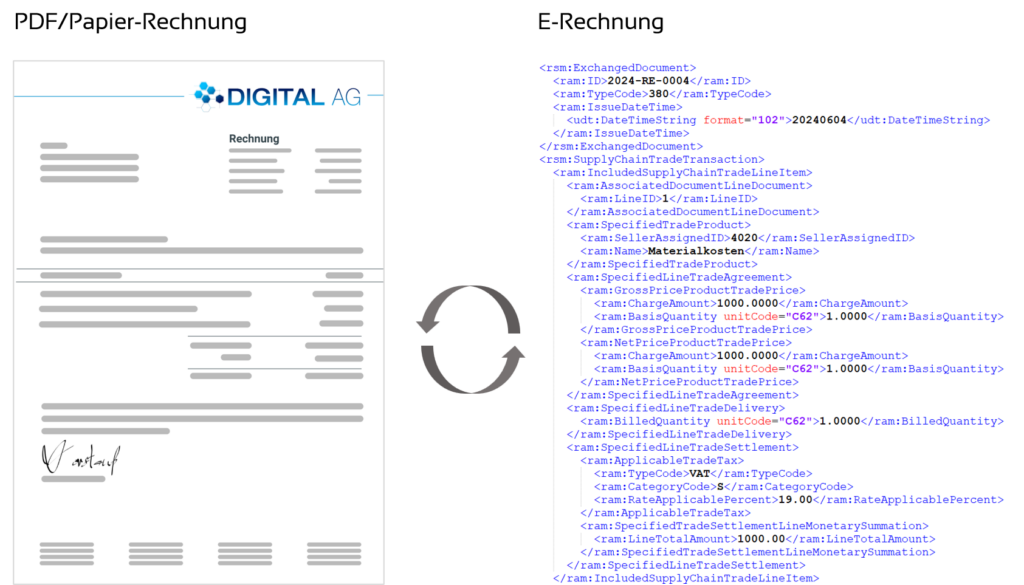
A paper or PDF invoice is not an e-invoice from the point of view of the legislator. The differences are explained in the following overview:
Paper invoice
The traditional paper invoice does not allow electronic processing, as the invoice would first have to be digitized via scan or photo. In order to be able to process the data further, the data contained on the invoice must be read out separately and entered into an accounting system.
PDF invoice
Although the PDF invoice is issued in a digital format, its main purpose is to present the invoice as “paper-like” as possible, i.e. as it would look in the form of a printed invoice. The PDF format is therefore suitable for human processing, where invoice information is read out manually. Additional text recognition (OCR software) is required for further electronic processing.
E-bill
The e-invoice is issued in accordance with a standard specified by the EU (EN-16931). This standard defines a structured data set based on the XML format. Invoices are thus represented as machine-readable code. This code can be created, sent and processed without media discontinuity. There are two e-invoice formats, ZUGFeRD and XRechnungen. The formats will be explained later.
The origin of the e-bill is the Growth Opportunities Act of the Federal Government In Article 23, it defines an e-invoice as follows:
“An electronic invoice is an invoice that is issued, transmitted and received in a structured electronic format and enables electronic processing. Another invoice is an invoice that is transmitted in another electronic format or on paper.”
Any invoice that does not meet the standard for e-invoices is summarized by the legislator under the term “other invoice”.
Obligation to e-bill
Purpose and background of the duty
Scope of the obligation
- both the supplier and the recipient are established in Germany and
- the turnover takes place in business transactions (B2B).
Transition periods
Until the end of 2026 Other invoices (PDF, paper, etc.) are permitted with the consent of the recipient.
Until the end of 2027 Other invoices are permitted with the consent of the recipient if the previous year’s turnover of the invoicing party
was less than EUR 800,000.
Requirements for an e-bill
Standard EN 16931
- The core model of the e-invoice (Core Invoice Model): It describes the information that every electronic invoice must contain.
- The syntactic bindings (syntax bindings): They describe how the core model can be represented in different electronic formats.
General requirements for an e-invoice
- Authenticity of origin: The identity of the invoice issuer must be ensured.
- Integrity of the content: The invoice details required under the Value Added Tax Act have not been changed.
- Legibility: The invoice must be legible to the human eye. E-invoices may have to be converted for this purpose.
- Invoices must also contain the following information (in accordance with Section 14 (4) UstG):
- the full name and address of the supplier and the recipient of the service,
- the tax number issued to the supplier by the tax office or the VAT identification number issued to him by the Federal Central Tax Office,
- the date of issue,
- a consecutive number with one or more series of numbers that is assigned once by the invoice issuer to identify the invoice (invoice number),
- the quantity and type (customary trade name) of the goods supplied or the scope and type of the other service,
- the date of the delivery or other service; in the cases of paragraph 5 sentence 1, the date of receipt of the consideration or part of the consideration, provided that the date of receipt is fixed and does not coincide with the date of issue of the invoice,
- the consideration for the delivery or other service, broken down according to tax rates and individual tax exemptions (Section 10), as well as any reduction in the consideration agreed in advance, unless it has already been taken into account in the consideration,
- the applicable tax rate and the amount of tax due on the consideration or, in the case of a tax exemption, an indication that a tax exemption applies to the delivery or other service,
- in the cases of Section 14b (1) sentence 5, a reference to the recipient’s obligation to retain the goods and services and
- in cases where the invoice is issued by the recipient of the service or by a third party commissioned by him in accordance with paragraph 2 sentence 2, the indication “credit note”.
Retention obligations for e-invoices
Formats of an e-bill
XInvoice
ZUGFeRD
ZUGFeRD stands for “Zentraler User Guide des Forums elektronische Rechnung Deutschland”. The format was developed together with associations, ministries and companies and is available free of charge. In contrast to XRechnung, ZUGFeRD is a hybrid format. This means that in addition to the XML file, a PDF file can also be sent, which displays the invoice in a conventionally readable format. However, it should be noted that the structured part of the invoice (i.e. the XML file) should be the leading part. With version 2.1.1, ZUGFeRD has integrated the requirements of XRechnung in a separate profile so that these are also accepted by public clients.
Opportunities and challenges
- Less error-prone: e-invoices can be read automatically. This avoids potential sources of error when entering data manually.
- Time-saving: Fully electronic transmission and processing saves time when digitizing or reading out invoices.
- Cost-saving: In addition to labor costs, there are no expenses for paper and postage.
- Process improvement: Receiving and sending invoices electronically makes it easier to record and evaluate financial data centrally.
- Research: How do e-invoices affect my business processes? When is my company obliged to receive and send e-invoices? What is the best way to implement this obligation technically? What needs to be considered in terms of data protection?
- Implementation: How do I introduce a system that can receive and send electronic invoices? How do upstream and downstream processes need to be adapted?
- Training: What are the guidelines for dealing with e-invoices? How can employees be prepared as well as possible for the changeover and familiarized with the new processes?
Software solutions for e-invoices
Moving away from Word and Excel for invoices
Invoice software versus complete solution
The first obvious step is to look for new software specifically for invoice management. This satisfies the new requirements, but also leaves some potential untapped, as other processes are linked to invoicing: For example, the recording of order or project times, the processing of tickets or controlling based on income and expenditure.
E-invoicing is therefore also an opportunity for companies to digitize business processes related to incoming and outgoing invoices. This is a further step towards the paperless office and offers companies a range of benefits:
- All-in-one concept: all business-relevant data is stored in one place, all processes take place online and on the basis of this data. No more isolated solutions, data disruptions or transmission errors.
- Simple and efficient processes: All important business processes take place on a common platform on which the entire team works. No more chain emails or paper printouts are necessary.
- Make business success measurable: All relevant data for your analyses is available in one place and can be incorporated into your business evaluations.
